Cybersecurity has become a key priority for businesses worldwide. With rising threats, new technologies, and higher expectations from leadership, how companies allocate their security budgets is more critical than ever.
The 2024 Security Budget Benchmark Summary Report offers a detailed look at current security budget trends, drawing insights from 755 CISOs surveyed between April and August 2024. Respondents represent a wide range of industries—from financial services to healthcare and technology—and companies of all sizes, from small firms under $100 million in revenue to giants exceeding $20 billion.
The results highlight how security spending is shifting due to growing threats and economic pressures, touching on slower budget growth, IT spending reallocation, and staffing challenges—essential insights for decision-makers managing today’s cybersecurity priorities.
Budget Growth and Security Spending in 2024
A key highlight in the report is the continued growth of security budgets, though at a slower pace compared to previous years. In 2024, budgets are projected to grow by 8%, a modest rise from 6% in 2023. While this shows improvement, it’s well below the sharp increases of 16% and 17% seen in 2021 and 2022.
The steady increase is driven by security breaches and risks tied to emerging technologies like AI, prompting some companies to allocate more funds. However, economic uncertainty and inflation have led to more cautious spending across different sectors.
Security budgets are also becoming a larger share of IT spending.
In 2024, security accounts for 13.2% of IT budgets, up from 8.6% in 2020. This growth reflects heightened awareness among leadership about the importance of cybersecurity, now seen as a core component of business strategy, particularly in data-sensitive industries like financial services and technology.
Industry-Specific Trends and Staffing Challenges
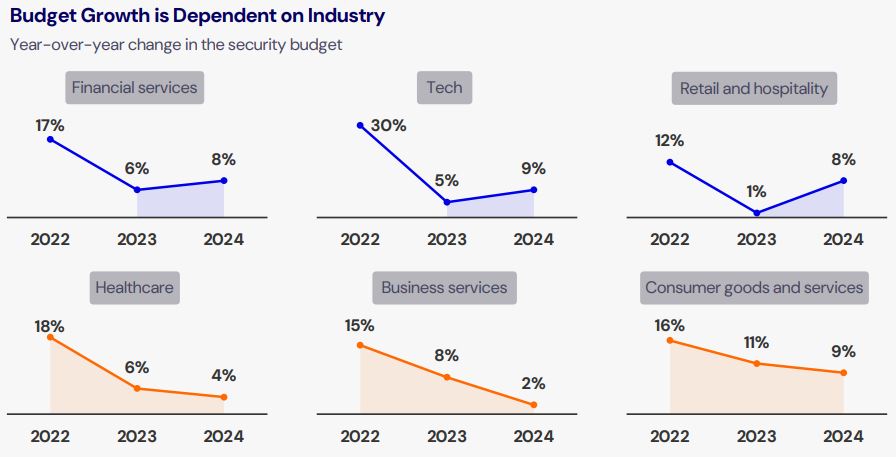
Budget growth varies widely across industries.
While some sectors like financial services and technology are seeing high single-digit growth in security budgets, others are not faring as well. For example, healthcare and business services have experienced a decline in their security budgets compared to 2023.
The 2024 Security Budget Benchmark Report
This discrepancy is driven by broader macroeconomic trends. Industries hit hardest by inflation and increased operational costs, such as consumer goods and healthcare, are cutting back not only on cybersecurity but across the board. In contrast, industries that rely heavily on digital transformation and data security, like tech and financial services, continue to invest more in their cybersecurity infrastructure.
Despite the increase in security budgets, staffing growth is on the decline.
In 2024, security headcount growth dropped to just 12%, down from 31% in 2022. Over one-third of CISOs reported no headcount increase at all, highlighting the trend of companies asking security teams to do more with less. This slowdown in hiring is a reflection of broader budgetary frugality. As companies tighten their belts, they are becoming more selective in allocating resources for recruiting.
However, this puts pressure on existing teams to maintain high levels of security with fewer people. Many CISOs are finding it increasingly difficult to secure additional funding for new hires, forcing teams to optimize and maximize their current capabilities.
Key Metrics and Allocation of Security Budgets
CISOs are relying on several key metrics to justify and guide their security budget decisions.
Among the most commonly used are “budget as a percentage of IT spend” and “budget as a percentage of annual revenue,” metrics favored by 67% and 52% of respondents, respectively.
The 2024 Security Budget Benchmark Report
Other frequently cited metrics include the security budget per employee and security headcount per IT employee. These metrics not only help CISOs benchmark their spending but also provide valuable data to justify further increases when necessary. The increasing reliance on standardized metrics is a sign of the growing maturity of cybersecurity as a core business function.
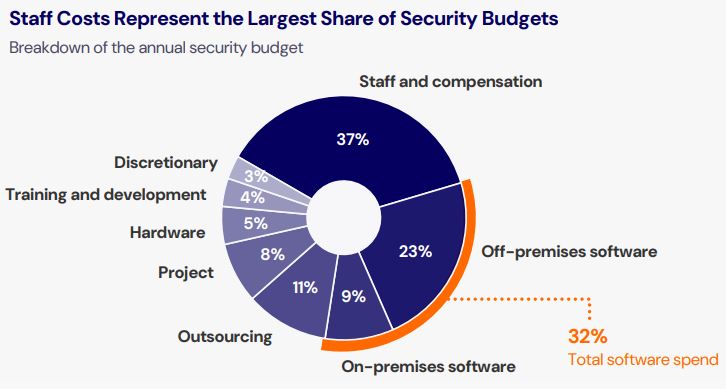
In terms of how security budgets are allocated, staffing and compensation remain the largest expenses, accounting for 37% of the total budget. Software spending, both off-premises and on-premises, also represents a significant portion of security budgets at a combined 32%. The report notes only marginal shifts in how budgets are distributed across different categories.
This suggests that, while overall spending is increasing, the fundamental priorities in security investments—people, technology, and services—remain consistent year over year.
Satisfaction and Challenges in Security Spending
A notable finding from the report is that despite the increase in security budgets, 28% of CISOs report being dissatisfied with their budget allocations. The majority, 52%, indicate they are either somewhat or very satisfied.
This level of satisfaction is often tied to the visibility and credibility of security leaders within their organizations.
Steve Martano, IANS Faculty member, highlights within the report that CISOs who can effectively communicate the importance of cybersecurity and engage in strategic discussions with leadership tend to secure better budget allocations and are more satisfied with their overall funding.
The Wrap
The 2024 Security Budget Benchmark Report highlights both monetary progress and challenges in the cybersecurity space. While security budgets continue to expand, driven by emerging risks and the increasing importance of cybersecurity within business strategy, the rate of growth has slowed, and staffing challenges persist.
These dynamics underscore the importance of strategic investment and careful resource allocation, especially in sectors like healthcare and business services where budget cuts are more prevalent. For CISOs, leveraging key metrics and securing visibility with leadership remains crucial in maintaining and justifying their financial needs.
As companies continue to navigate these challenges, the ability to do more with less while staying ahead of threats will determine who thrives in the face of uncertainty.